Insurance options for small business owners sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with formal and friendly language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Small business owners face a myriad of risks in today’s competitive landscape, making it crucial to have the right insurance coverage to protect their assets and livelihood. This article delves into the various insurance options tailored for small businesses, highlighting their importance and benefits.
Overview of Insurance Options for Small Business Owners
Insurance is a crucial aspect of protecting small businesses from unexpected risks and liabilities. There are various types of insurance options available that cater to the specific needs of small business owners.
Types of Insurance for Small Businesses
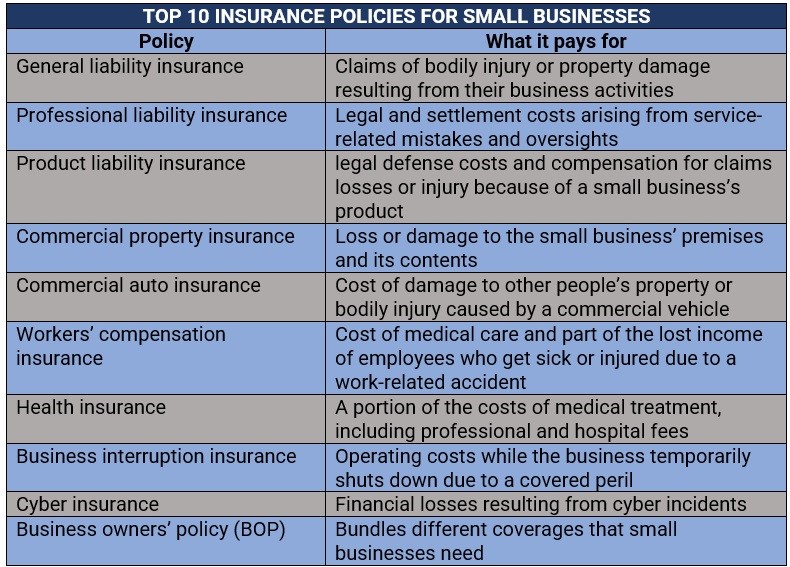
- General Liability Insurance: This policy provides coverage for third-party bodily injuries, property damage, and advertising injuries.
- Property Insurance: Protects your business property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and other assets, from damages due to fire, theft, or other covered perils.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Also known as errors and omissions insurance, this policy covers claims of negligence or inadequate work performance.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: This insurance is mandatory for businesses with employees and provides coverage for work-related injuries and illnesses.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Helps cover lost income and extra expenses if your business is unable to operate due to a covered peril.
Importance of Insurance Coverage for Small Businesses
Having the right insurance coverage can help small business owners mitigate financial risks and protect their assets. In the event of unexpected events like lawsuits, natural disasters, or accidents, insurance can provide the necessary support to keep the business running smoothly.
Examples of Common Insurance Policies Tailored for Small Businesses
- Business Owner’s Policy (BOP): A comprehensive package that combines general liability, property, and business interruption insurance tailored for small businesses.
- Commercial Auto Insurance: Provides coverage for vehicles used for business purposes, protecting against accidents, theft, and other damages.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: Protects businesses from cyber threats, data breaches, and other cyber-related risks.
- Commercial Umbrella Insurance: Offers additional liability coverage beyond the limits of primary insurance policies to protect against catastrophic losses.
General Liability Insurance
General liability insurance is a type of coverage that helps protect small businesses from financial losses resulting from claims of bodily injury, property damage, advertising mistakes, and other related incidents. It is an essential policy that can safeguard businesses from lawsuits and other liabilities that may arise during their operations.
Role of General Liability Insurance
General liability insurance plays a crucial role in protecting small businesses by covering legal fees, medical expenses, and damages in case of lawsuits or claims filed against the business. This coverage provides financial support and peace of mind to business owners, ensuring that they can continue their operations without the fear of significant financial losses.
Scenarios where General Liability Insurance is Beneficial, Insurance options for small business owners
- Customer Slips and Falls: If a customer slips and falls on your business premises and sues for medical expenses, general liability insurance can cover the costs.
- Property Damage: In case your business accidentally damages someone else’s property, this insurance can help cover the repair or replacement costs.
- Advertising Errors: If your business faces a lawsuit due to misleading advertising or copyright infringement, general liability insurance can provide legal protection.
Comparison of Coverage Limits and Premiums
When considering general liability insurance plans, it’s essential to compare different coverage limits and premiums to find the most suitable option for your small business. Higher coverage limits usually mean higher premiums, but they also offer more comprehensive protection. It’s crucial to assess your business’s specific needs and risks to determine the right balance between coverage and cost.
Business Property Insurance: Insurance Options For Small Business Owners
Business property insurance provides coverage for the physical assets of a small business, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and furniture. In the event of a covered loss such as fire, theft, or vandalism, this insurance helps to repair or replace the damaged property, ensuring that the business can continue its operations smoothly.
Coverage Provided by Business Property Insurance
Business property insurance typically covers the following:
- Buildings: Provides coverage for the physical structure of the business premises.
- Equipment: Covers machinery, tools, and other equipment used in the business.
- Inventory: Protects the goods and products held for sale or distribution.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Includes coverage for office furniture, shelving, and other fixtures.
Examples of Crucial Situations
Imagine a small retail store experiencing a break-in resulting in stolen merchandise and damage to the store. Business property insurance would help cover the cost of replacing the stolen goods and repairing the store, allowing the business to resume its operations.
Determining the Value of Assets
Before purchasing business property insurance, small business owners need to determine the value of their assets accurately. This involves taking an inventory of all physical property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and furniture. The value of these assets will help determine the appropriate coverage needed to protect the business adequately in case of a loss.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance
Workers’ compensation insurance is a crucial coverage for small businesses that have employees. It provides protection for both the employees and the business in the event of work-related injuries or illnesses.
Importance of Workers’ Compensation Insurance
- Ensures medical treatment and wage replacement for employees who are injured on the job.
- Helps protect the business from costly lawsuits related to workplace injuries.
- Demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being and safety, which can boost morale and productivity.
Legal Requirements and Benefits
Workers’ compensation insurance is mandatory in most states for businesses with employees. By carrying this coverage, businesses can:
- Comply with state laws and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
- Provide financial protection for employees and their families in case of work-related accidents.
- Potentially reduce the risk of lawsuits from employees seeking compensation for workplace injuries.
Premium Calculation
Workers’ compensation insurance premiums are calculated based on several factors, including:
- The type of work performed by employees and associated risk levels.
- The number of employees covered by the policy.
- The business’s claims history and safety record.
Insurance companies use these factors to assess the level of risk the business presents and determine the appropriate premium to charge.
Professional Liability Insurance

Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions insurance, provides coverage for businesses and professionals in case they are sued for negligence, errors, or omissions in the services they provide.
Professions/Industries Requiring Professional Liability Insurance
- Medical professionals such as doctors, nurses, and therapists
- Legal professionals including lawyers and consultants
- Accountants and financial advisors
- Technology consultants and IT professionals
Claims Covered under Professional Liability Insurance
- Alleged negligence or errors in professional services
- Failure to deliver services as promised in a contract
- Legal defense costs in case of a lawsuit
- Claims of misinformation or professional advice leading to financial loss
Health Insurance Options for Small Business Employees
When it comes to providing health insurance options for small business employees, there are a few key considerations to keep in mind. Offering health insurance benefits can play a significant role in attracting and retaining top talent, as well as promoting the overall well-being of your workforce.
Group Health Insurance vs. Individual Health Insurance
Group health insurance is typically offered by employers to their employees, providing coverage to a group of people under one policy. This can often be a more cost-effective option compared to individual health insurance plans, as the risk is spread out among the group. On the other hand, individual health insurance allows employees to choose their own plans based on their specific needs, but it can be more expensive compared to group coverage.
Impact of Offering Health Insurance Benefits
- Improves Employee Retention: Providing health insurance benefits can increase employee loyalty and reduce turnover rates, as employees are more likely to stay with a company that offers valuable benefits.
- Enhances Recruitment Efforts: Offering health insurance can also attract top talent during the recruitment process, as job seekers often prioritize companies that provide comprehensive benefits packages.
- Promotes Employee Well-being: Access to health insurance can help employees take care of their health and well-being, leading to increased productivity and job satisfaction.
Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance is a type of insurance coverage designed to protect businesses from internet-based risks and cyber threats in the digital age. It provides financial protection in the event of data breaches, cyber attacks, or other cyber incidents that could compromise sensitive information or disrupt business operations.
Types of Cyber Threats Covered
- Ransomware Attacks: Cyber insurance can cover the costs associated with ransom payments and data recovery in case of a ransomware attack.
- Data Breaches: This coverage helps businesses manage the costs of notifying affected parties, credit monitoring services, and legal fees resulting from a data breach.
- Business Interruption: Cyber insurance can provide coverage for revenue loss and extra expenses incurred due to a cyber attack that disrupts business operations.
Examples of Cyber Incidents
Example 1: A small business’s website is hacked, and customer data is stolen. Cyber insurance would cover the costs of notifying customers, investigating the breach, and potential legal expenses.
Example 2: A ransomware attack encrypts a small business’s critical files, leading to operational downtime. Cyber insurance would help cover the costs of data recovery, ransom payment, and business interruption losses.
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, navigating the world of insurance options for small business owners can be daunting, but with the right information and guidance, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions to safeguard their businesses. Whether it’s general liability insurance, business property insurance, or professional liability coverage, each policy plays a vital role in mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity. By understanding the significance of these insurance options, small business owners can protect their ventures and thrive in an ever-evolving market.
Helpful Answers
What are the key factors to consider when choosing insurance options for small business owners?
When selecting insurance for your small business, it’s essential to assess your specific needs, industry risks, budget constraints, and legal requirements to determine the most suitable coverage.
Is health insurance mandatory for small business owners to provide for their employees?
While health insurance isn’t legally required for small businesses, offering this benefit can enhance employee satisfaction, retention, and overall well-being, contributing to a positive work environment.
How can small business owners mitigate cyber risks without cyber insurance?
Small business owners can enhance cybersecurity measures by training employees on best practices, implementing robust IT protocols, regularly updating software, and conducting risk assessments to prevent cyber threats.